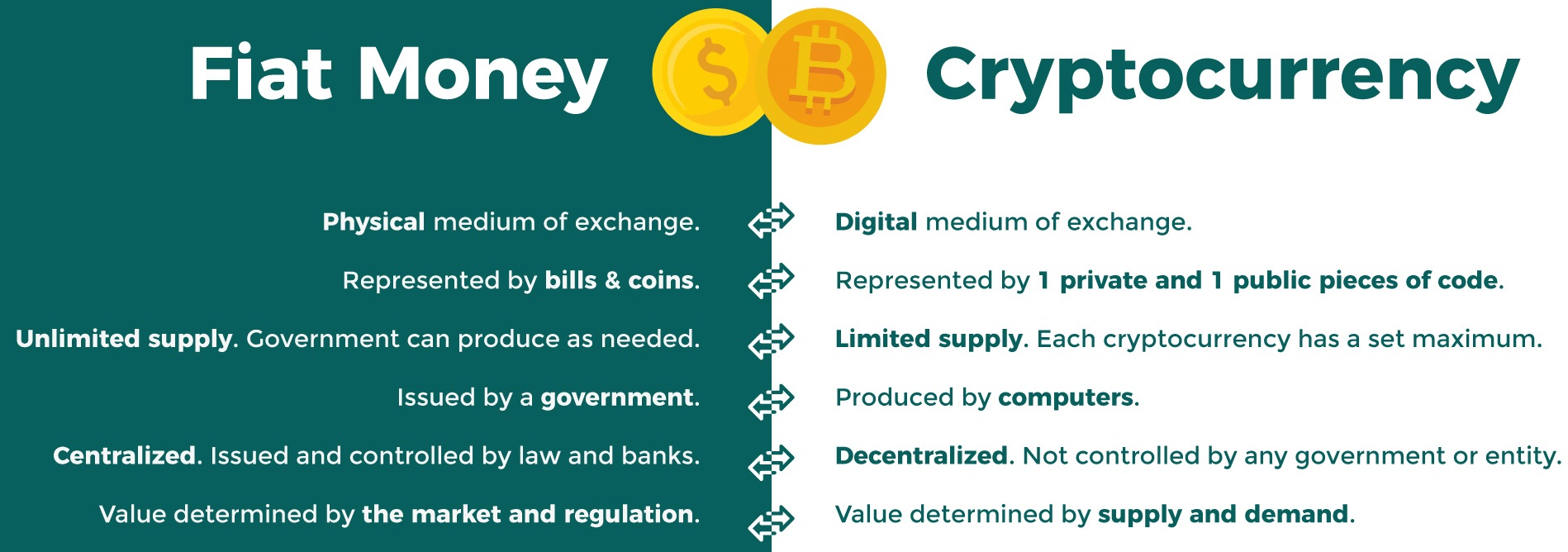
What is the issue?
The development of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies in a little over a decade has spawned a parallel universe of alternative financial services. Here is a look at them.
What do crypto businesses offer?
- Generally, lending and borrowing.
- Earn interest on holdings of digital currencies, often a lot more than on cash deposits in a bank.
- Borrow with crypto as collateral to back a loan. Crypto loans generally involve no credit checks as transactions are backed by digital assets.
- E.g., In a BlockFi interest account, depositors can earn a yield 100 times higher than on average bank accounts.
- [BlockFi is a secured non-bank lender that offers cryptoasset-backed loans to cryptoasset owners.]
Benefits
- Fosters financial inclusion.
- Unusually high return on their holdings for consumers.
- Provide financial stability for customers in countries with volatile government-issued currencies.
Why such high yields?
- Crypto outfits pool deposits to offer loans and give interest to depositors, just as traditional banks.
- But by law, banks are required to have minimum reserves as a safety backup.
- Unlike this, crypto banks do not have the reserve requirements; the institutions they lend to can take risky bets.
- E.g., BlockFilends to hedge funds and other institutional investors who exploit flaws in crypto markets to make fast money without actually holding risky assets.
- Other risks: Cyberattacks, extreme market conditions, or other operational or technical difficulties that could lead to a temporary or permanent halt on withdrawals or transfers.
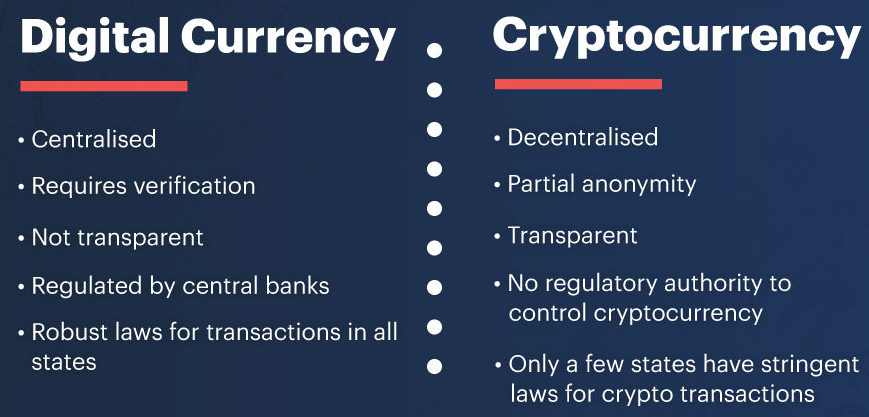
What is a stablecoin?
- Crypto is very volatile, making it less practical for transactions like payments or loans.
- But Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies linked to stable assets, commonly the dollar. Popular dollar-tied tokens include Tether and USD Coin.
- It aims to do in digital form what government money does.
- They provide the steady value of government-issued money in digital form for blockchain transactions, but they are issued by private entities.
Risks
- Stablecoin issuers hold and monitor reserves, just as central bankers manage supply and demand.
- But there is no guarantee they actually hold the one-to-one dollar backing they claim.
- So, a sudden surge in withdrawals could lead to a collapse in one of those assets, putting clients and the broader economy at risk.
- Also, a central bank digital currency would render stablecoins irrelevant.
What is a central bank digital currency?
- Central bankers are examining the potential for issuance of a government-issued cryptocurrency.
- That would offer the convenience of crypto with the reliability of money controlled by a central bank.
- But governments catching up to the innovations in the market for years will be a challenge.
What is DeFi?
- Decentralized finance, or DeFi, refers to an alternative finance ecosystem where consumers transfer, trade, borrow and lend cryptocurrency.
- Financial products become available on a public decentralized blockchain network, independently of traditional financial institutions and the regulatory structures.
- DeFi aims to “disintermediate” finance, using computer code to eliminate the need for trust and middlemen from transactions.
- It’s a computer-controlled market that automatically executes transactions.
- In contrast, centralized finance, or CeFi, businesses more closely resemble traditional finance, or TradFi.
- Here, consumers enter into an agreement with a company like BlockFi that collects information about them, requires them to turn over their crypto and also serves as a central point for regulators.
What could be done in the future?
- A new regulating approach for adapting to the new technology demands.
- E.g., Requirements like code audits and risk parameters, instead of mandating that DeFi protocols maintain the reserves of a bank and collect customer information.
- Using artificial intelligence and data analysis to monitor suspicious activity and tracking identity to fight financial fraud.
Source: The Indian Express
