Why in news?
For the third time since early June 2020, China repeated its claim that Bhutan’s eastern boundary was a “disputed” area.
- Its first claim was at a UNDP-led Global Environment Facility (GEF) conference on 2-3 June 2020.
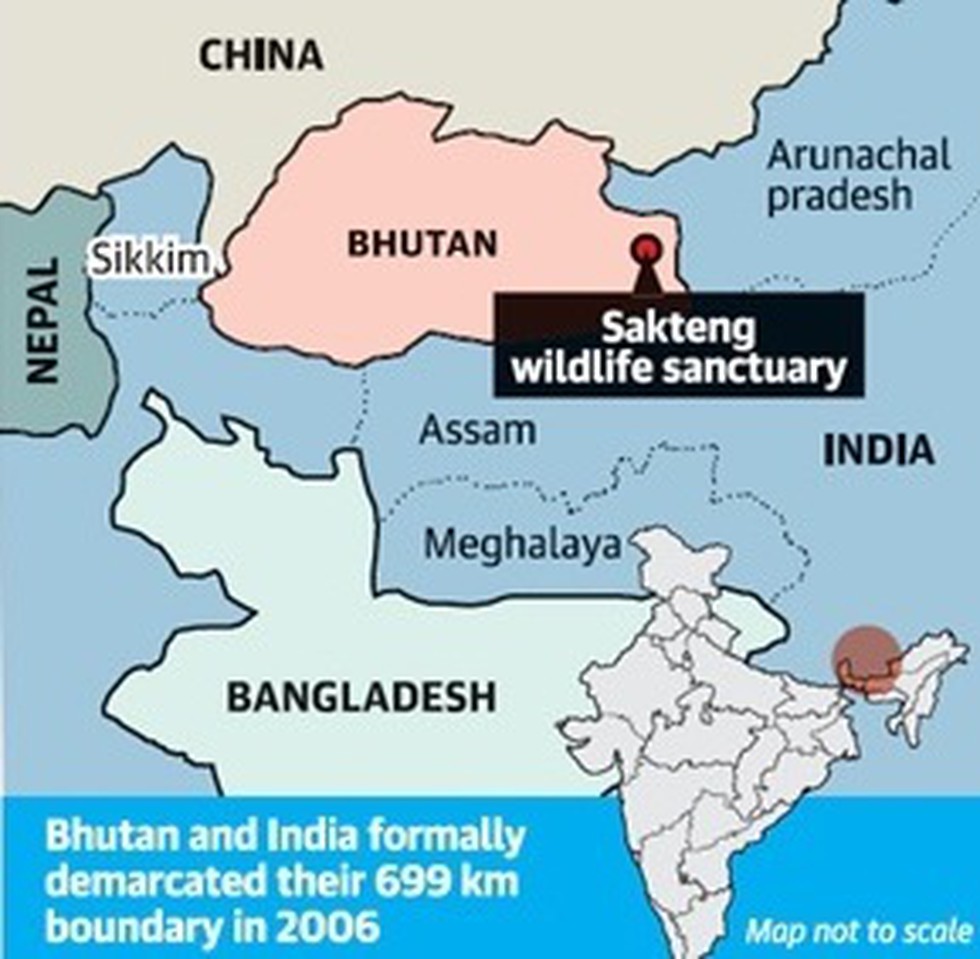
- Back then, Chinese representative tried to stop funding for the Sakteng forest reserve in Bhutan’s eastern district of Trashigang.
- The forest, notably, has a common boundary with Arunachal Pradesh’s Tawang district.
Why are the claims unreasonable?
- China has not objected earlier to funding provided to the sanctuary at the GEF.
- The Trashigang area does not share a boundary with China.
- Whatever the origins of the claim, Chinese officials have not raised the eastern boundary in 24 rounds of talks with Bhutan, that began in 1984.
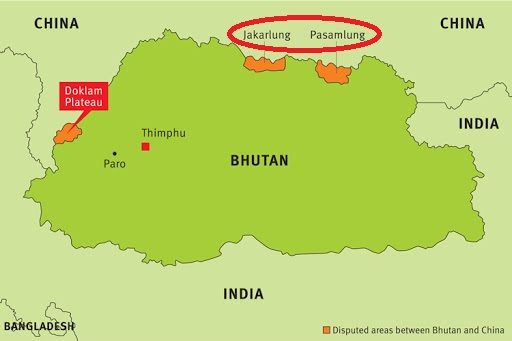
- Thus far, talks have been only about the Pasamlung and Jakarlung valleys in Bhutan’s north.
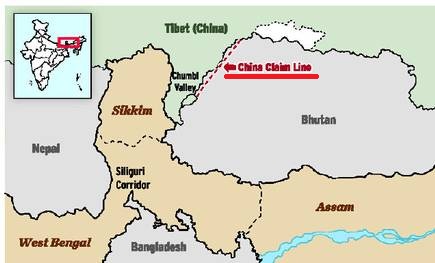
- The Doklam and other pasturelands to the west are also part of the talks; the areas that come up to the tri-junction point with India.
What are China's suggestions and Bhutan's response?
- China referred to a “package solution” for the dispute.
- It seems to refer to an offer made in the 1990s to swap the northern and western areas.
- But this is something that Bhutan rejected, given India’s concerns.
- Bhutan’s response at the start was to reject China’s claim at the GEF, and it was able to secure the funding.
- Subsequently the Bhutanese Embassy in Delhi served a démarche to the Chinese Embassy.
- [Bhutan does not have diplomatic relations with China.]
- But the Chinese MFA (Ministry of Foreign Affairs) kept repeating the claim.
- Bhutan has now appeared to take a firm view of China’s claims.
- It has said that all disputes would be taken up in the next round of China-Bhutan talks.
- [The last round of talks was in 2016.
- Talks have been put off due to the Doklam stand-off in 2017, elections in 2018, and the recent pandemic.]
What possibly are China's motives?
- In Bhutan's case, the Chinese claim is seen much as a pressure tactic.
- It is an attempt to hurry the scheduling of the next meeting (China-Bhutan).
- It could also be an attempt to gain leverage in the boundary talks.
- India, on the other hand, is already dealing with Chinese aggression across the Line of Actual Control.
- So, the Sakteng claim could be a diversionary tactic.
- It could also be a move aimed at creating a divide between India and Bhutan.
- More significantly, by claiming Bhutan’s eastern boundary, China is attempting to strengthen its claims over Arunachal Pradesh.
What is the way forward?
- Despite Beijing’s repeated statements on the boundary issue, both Thimphu and New Delhi have chosen not to react in a rash manner.
- The repetition of its “package” offer is worrying as it implies that Beijing is not giving up its push for the Doklam plateau.
- Notably, China has consolidated its military infrastructure in Doklam.
- It would like to inch towards India’s Chumbi valley, a strategically sensitive location.
- Given all these, New Delhi and Thimphu must stay the course, no matter what Beijing’s plans are behind its new claims in Bhutan.
- They must move ahead with the close cooperation and complete understanding they have shared for decades.
Source: The Hindu
