THE HINDU – CURRENT NOTE 19 January
G.S-01
 Jaipur Lit Fest’s theme is ‘Freedom to dream’
Jaipur Lit Fest’s theme is ‘Freedom to dream’

- The 10th edition of the Jaipur Literature Festival (JLF) beginning at the historic Diggi Palace situated in the heart of Jaipur.
- “Freedom to dream: India at 70” will be the theme of the event.
- The five-day festival will witness participation of over 250 authors, thinkers, politicians, journalists and popular culture icons, while the number of audience is expected to surpass last year’s figure of 3.30 lakh.
Discussion on RSS:
- JLF will witness intense participation of speakers discussing the topics ranging from civil wars and cultural appropriations to women’s empowerment, experiments with truth and understanding aesthetics.
- A session devoted to the theme, “Saffron and the Sangh, which will have Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh leaders Dattatreya Hosabale and Manmohan Vaidya in conversation with Pragya Tiwari, has already generated curiosity in view of the RSS ideology being discussed for the first time in the event.
 Ramjas concludes centenary celebrations
Ramjas concludes centenary celebrations

- Ramjas College completed 100 years of fulfilling their promise of quality education. The College, situated on the North Campus.
- Ramjas College is one of the oldest educational institutes, founded by Rai Kedarnath.
- The college was named in memory of Lala Ramjas, the father of Rai Kedarnath.
- The college was set up with the aim to cater to the educational needs of middle and lower middle sections of the society.
- It was inaugurated by Mahatma Gandhi at its Old campus in Anand Parbat. Many students of the collage participated in the Quit India Movement.
 TN takes jallikattu issue to PM
TN takes jallikattu issue to PM

- CM O. Panneerselvam leaves for Delhi to take up the issue with Prime Minister Narendra Modi after pro-jallikattu (bull-taming sport) protests swell into a mass movement.
- ‘It is our right’
- Representatives refused to call off their agitation as they were waiting the outcome of the scheduled talks between Mr. Modi and Mr. Panneerselvam.
- The Protest:
- Initiated on social media platforms, the protests which were initially confined to the college student community and rural folk, overnight turned into a mass movement of sorts.
- The protesters demanded the lifting of the ban on Jallikattu or an ordinance. They also sought a ban on PETA.
- The Protest spawned overnight at the Marina in Chennai, Alanganallur in Madurai, VOC Grounds in Coimbatore and other districts.
- Jallikattu supporters attack police team, damage three vehicles when law enforcers prevented them from organising jallikattu near St Antony’s Church at Kandupatti after celebrating ‘Samathuva Pongal’.
G.S-02
 Death by adulterated food may lead to life term
Death by adulterated food may lead to life term

- The Law Commission of India has recommended life imprisonment for traders, businessmen and shopkeepers found guilty of the death of their customers by intentionally selling them adulterated or “noxious” food and drink.
- The suggested amendments in penal law for food adulteration is the focus of the Commission’s 264th report titled ‘The Criminal Law (Amendment) Bill 2017 (Provisions dealing with Food Adulteration)’.
- Victims of greed:
- Lives of pregnant women and children in anganwadis and government schools, fall victim to the greed of individuals looking for a slight margin by selling adulterated food and drinks to unsuspecting consumers.
- Weak Law:
- Currently, under Sections 272 and 273 of Indian Penal Code, 1860, the guilty get away with either a fine of Rs. 1000 or, rarely, an imprisonment of 6 months for selling adulterated or noxious food and drink with fatal results.
- Supreme Court direction to the government inSwami Achyutanand Tirth versus Union of India, which dealt with rampant adulteration in milk supplied to school students, for urgent amendments in the penal law and bring punishment on food adulteration up to the times.

- Paltry fine:
- A fine of Rs. 1000 or a rare six months in prison was hardly a deterrent for a crime causing deaths and grievous injury to a cross-section of the society.
- Commission’s Stand:
- The government had in turn referred the matter to the Law Commission to frame the amendments.
- The Commission besides, life imprisonment, recommended that the guilty should pay the victim’s family a sum of Rs. 10 lakh as fine for his crime.
- The Commission borrowed the example of three States – Orissa, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal – to recommend life imprisonment to those found guilty of causing death by food adulteration.
- The Law Commission recommendations are now on the government’s table, awaiting a decision.
 India, Sri Lanka in talks on port
India, Sri Lanka in talks on port

- Sri Lanka is in talks to offer the port of Trincomalee to India, the decision on offering the port to India will be taken soon.
- Trincomalee has been on the table for sometime as Sri Lanka wants to maintain a neutral stand and provide equal access to its ports to both China and India.
- Hambantota hurdles:
- Hambantota port in Sri lanka being developed by the China, who carried out major infrastructural work at the Hambantota port in southern coast of the island nation, has put a heavy burden on the country.
- Sri Lanka is willing to address India’s concerns on the visit of Chinese nuclear submarines to Sri Lanka.
- Debt Burden:
- The port of Hambantota was conceived as a major Sri Lanka-China project during the presidency of Mahinda Rajapakse, but the controversy around the debt burden has slowed down the project.
- Colombo is aware of its responsibilities in the Indian Ocean region, and is committed to freedom of navigation.
 Respect sovereignty, India tells China
Respect sovereignty, India tells China
- Asserting its territorial sovereignty, India said at second edition of the Raisina Dialogue that the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passes through its territory.
- China and Pakistan have fast-tracked work on CPEC, a large part of which passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir. Once completed, CPEC will provide an all-weather energy route for China from the Gulf.
- Reports of China-Pakistan naval cooperation in Gwadar port of Balochistan, which will serve as the entry point to CPEC increases India’s concerns.
- Dynamic factor:
- China’s rise was a major “dynamic” factor in the Asian affairs and reminded the audience that differences with China had not gone away.
- China’s overall broadening of ties, especially in business and people-to-people contacts, has been overshadowed by differences on certain political issues.
- Differences with China:
- CPEC and the “political issues” are significant as both India and China have dealt with the differences over the last several months.
- India’s membership bid in the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) was scuttled by China in the year 2016.
- China’s territorial assertion over Asia, received a jolt in July 2016 when the Permanent Court of Arbitration gave an adverse verdict on the South China Sea issue.
- India’s position on South China Sea was in sync with the international position.
 Uttar Pradesh registers increase in number of out-of-school children
Uttar Pradesh registers increase in number of out-of-school children

Pratham annual report says the State also has a low attendance rate, along with Bihar & Manipur.
- Pratham’s Annual Status of Education (Rural) report for 2016:
- In U.P the fraction of out-of-school children between six and 14 years of age climbing to 5.3 % from 4.9 % between 2014 and 2016.
- Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh — also share the dubious distinction, with fractions of out-of-school children climbing from 3.4 % to 4.4 % in the former, and from 2 per cent to 2.8 % in the latter in the same time span.
- Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Manipur, West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh has low attendance rates of children, at 50-60 %.
- The all-India enrolment ratio for the age-group of six to 14 has slightly improved from 96.7 % in 2014 to 96.9 % in 2016.
- The proportion of out-of-school girls between 11 and 14 years of age still stays higher than 8% In Uttar Pradesh (9.9 % ), Rajasthan (9.7 % ) and Madhya Pradesh (8.5 %) but some States continue to under-perform.
- Usable toilet availability is rising, with 68.7 % schools now having usable toilets as against 47.2 % in 2010. Just 3.5 % schools visited across India had no toilets in 2016.
- There was nationally no increase in private school enrolment between 2014 and 2016.
- Areas of concern: in reading and arithmetic ability
- English-reading ability:
- At Class 3 students at the all-India level has increased, with 32 % students in 2016 — compared with 28.5 % in 2014 — being able to read simple words.
- 2 % Class 8 students could read simple sentences in 2009, the number was 46.7 % in 2014 and 45.2 % in 2016.
- The ability to read English at Class 5 level, however, stays unchanged.
- English-reading ability:
- No computers:
- In Rural Schools just 20 % schools had computers in 2016, marginally higher than 19.6 % in 2014.
- In Kerala 89% schools had computers, Gujarat2%, Maharashtra 55.1% Tamil Nadu 57.3%.
 Court decrees can’t be flouted, warns SC
Court decrees can’t be flouted, warns SC

- Supreme Court warned on decrees passed in the Sutlej-Yamuna Link (SYL) canal dispute between Punjab and Haryana cannot be flouted.
- The interim order of status quo will continue which asked the Centre and Punjab to file their replies to Haryana’s plea seeking compliance of court’s order.
Status quo:
- The reports of the Union Home Secretary, Chief Secretary of Punjab and Director General of Police of Punjab, who were appointed as court receivers of the land and other properties of the canal, have indicated that status quo has been maintained.
- Haryana has not challenged the Punjab Termination of Agreement Act, 2004, and therefore it has not been set aside till now.
- The effect of the apex court’s decree cannot be there unless the Act passed by legislature is nullified.
The answers to Presidential reference fell under the advisory jurisdiction and hence the court has not set aside the Act.
G.S-03
 Rs. 9.2 lakh cr. back in circulation: RBI chief
Rs. 9.2 lakh cr. back in circulation: RBI chief

- Urjit Patel Governor RBI told the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance that about Rs. 9.2 lakh crore had been put back in circulation since the demonetisation on November 8.
- After 8th November 86% (Rs. 15.44 lakh crore) — of currency notes in circulation till then strucked.
- On demonetised currency that had been deposited back in banks still on continuing. RBI rejected media reports that 97% of the demonetised currency was back in the system.
- RBI said figures would need to be reconciled with the physical cash balances to eliminate accounting errors/possible double counts, etc without which estimates may not indicate actual numbers.
- The liability of the RBI has not been extinguished, denying the government the fiscal space for greater social sector spending.
- The printing of Rs. 2,000 notes had begun in June 2016.
- The demonetisation decision by the government and the RBI — taken at the behest of the govt. — took about one year to plan.
- Once the money has passed through the system, it will be scrutinised in order to catch the wrongdoers.
 Regional connectivity plan nets proposals to revive 65 airports
Regional connectivity plan nets proposals to revive 65 airports

- The Airports Authority of India has received 45 proposals from 11 bidders covering more than 200 routes for the regional connectivity scheme.
- Operators Interest
- The operators have submitted plans covering 65 airports, out of which 52 are un-served airports which haven’t seen a single flight for more than a year and the remaining 13 are under-served airports where less than seven commercial flight departures take place in a week.
- Operators interested in Underserved airports: Kadapa in Andhra Pradesh, Jamnagar and Bhavnagar in Gujarat, Jorhat in Assam, Kullu in Himachal Pradesh, Diu, Puducherry, Agra in Uttar Pradesh, Pant Nagar in Uttarakhand, Gwalior in Madhya Pradesh and Durgapur in West Bengal.
- Some of the unserved airports, proposed to be revived for regional flights, include Bilaspur and Jagdalpur in Chhattisgarh, Jamshedpur in Jharkhand, Jeypore and Jharsuguda in Odisha, Jalandhar in Punjab, Kandla in Gujarat, Kolhapur and Latur in Maharashtra.
- The Scheme:
- As per the scheme, the Centre will subsidise the losses incurred by airlines flying out of dormant airports, to allow airlines to charge ₹2,500 for an hour’s flight to passengers.
- About 80% of the subsidy will be collected by charging a levy of up to ₹8,500 on each departing flight of domestic airlines and the rest 20% will come from the respective state governments.
- The Centre has now invited counter-bids against these initial proposals and will accept them till February 1. The routes or networks would be awarded to bidders who quote the lowest requirement of Viability Gap Funding (VGF) against such routes.
 Prototype of super, super computer in 2017
Prototype of super, super computer in 2017

- To win a global race to be the first to build a machine capable of a billion, billion calculations per second, China plans to develop a prototype exascale computer by the end of the year.
- China built the world’s fastest supercomputer, the Sunway TaihuLight machine, in June last year.
- It used only locally made microchips, making it the first time a country has taken the top spot without using U.S. technology.
- Of the top 10 fastest computers, two are in China and five in the US as of November,2016.
- The Exascale Computers:
- Exascale computers are even more powerful, and can execute at least one quintillion (a billion billion) calculations per second.
- A complete computing system of the exascale supercomputer and its applications can only be expected in 2020, and will be 200 times more powerful than the country’s first petaflop computer Tianhe-1.
- The exascale computer could have applications in big data and cloud computing work, he added, noting that its prototype would lead the world in data transmission efficiency as well as calculation speed.
- Despite some gains the country’s scientific output still lags behind, and its universities fare poorly in global rankings.
 Trump’s hair inspires naming of tiny moth
Trump’s hair inspires naming of tiny moth
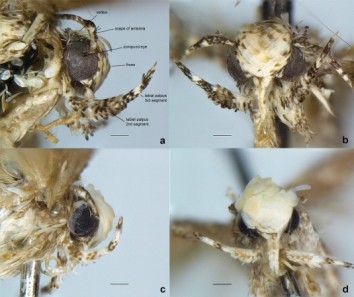
- Scientists have named a species of moth after U.S. President-elect Donald Trump.
- By naming this species after the 45th President of the U.S it bring some public attention to and interest in the importance of alpha-taxonomy in better understanding the neglected micro-fauna component of the North American biodiversity.
- About Neopalpa donaldtrumpi:
- The adult of the species stands out with yellowish-white scales on the head.
- The discovery of this distinct micro-moth in the densely populated southern California.
- The twirler moth lives in a substantially urbanised and populated habitat, stretching across the states of California in the U.S. and Baja California in Mexico. The habitat is under serious threat.
- The moth [Neopalpa donaldtrumpi], specimen already exists in the collections of the Bohart Museum of Entomology at the University of California.
 2016 was the hottest year on record
2016 was the hottest year on record

- Temperatures spiked to new national highs in parts of India, Kuwait and Iran, while sea ice melted faster than ever in the fragile Arctic, said the report by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
- Taking a global average of the land and sea surface temperatures for the entire year, NOAA found the data for “2016 was the highest since record keeping began in 1880”.
- The global average temperature last year was 0.94˚C above the 20th century average, and 0.04˚C warmer than in 2015.
- A separate analysis by the U.S. space agency NASA also found that 2016 was the hottest on record.
The Findings:
- Atmospheric concentrations of both carbon dioxide and methane reached record levels. The main reason for the rise is the burning of fossil fuels like oil and gas, which send carbon dioxide, methane and other pollutants known as greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere and warm the planet.
- Since the start of the 21st century, the annual global temperature record has been broken five times [2005, 2010, 2014, 2015 and 2016]
- The Pacific Ocean warming trend of El Nino, which experts say exacerbates the planet’s already rising warmth.
- Unusual spikes in temperature were seen in Phalodi, India, which reached 51˚C on May 19 — marking India’s hottest temperature ever. Dehloran, Iran hit 53˚C on July 22, a new national record. Mitribah, Kuwait hit an all-time high of 54˚C on July 21, which may be the highest temperature ever recorded in all of Asia.

